
WHAT IS CULTURAL HERITAGE?
Cultural heritage is the set of assets acquired by inheritance, that have to do with the culture of a nation, city, society… their lifestyles, customs, knowledge and developments. It implies the concept cultural identity.
Cultural identity is the set of objects with historical or artistic value (monuments) but also any expression, manifestation or significant testimony of human culture with documentary capacity.
There was a need to recover and reconstruct the signs specially after the Secon World War.
Traditional history is focused on important events, therefore, the monument was the best representation of these. However, new history centers it’s interest in the man and his existence, and cultural assets are the best representation.
In 1972 the UNESCO proposed a new classification of cultural assets which consists on
- Monuments: architecture, sculpture, painting, archeology, caverns inscriptions…
- Sets: grups of constructions which have a value due to its integration with the landscape
- Places: works of man and nature
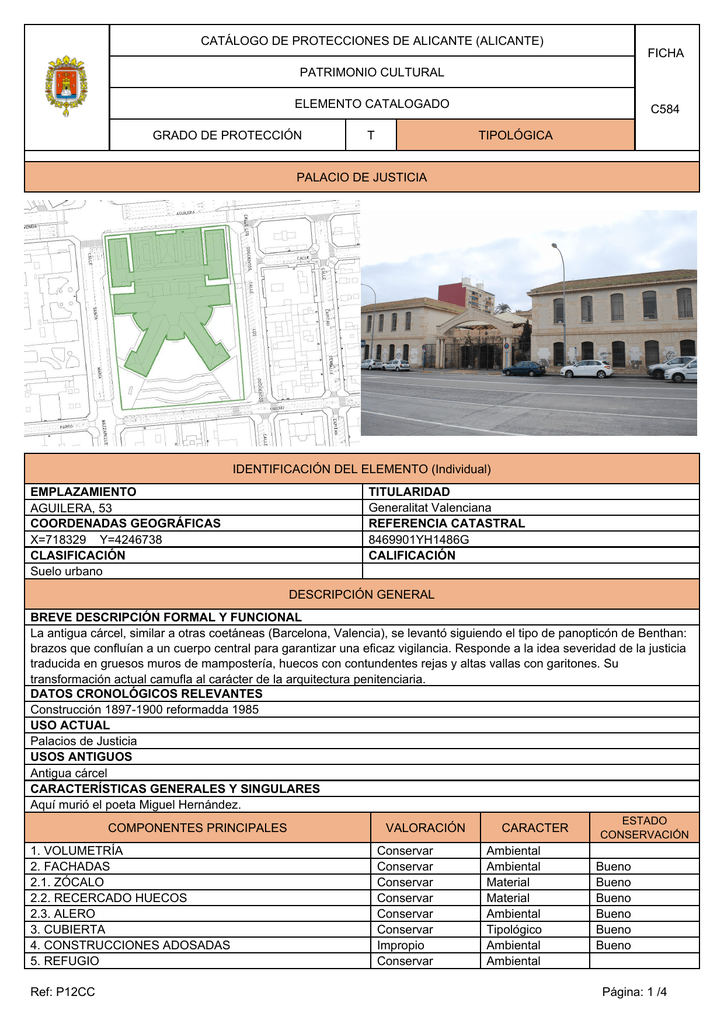
The maximum protection figure is introduced by the Law of Patrimonio Histórico Español as the BIC.
The following are considered cultural assets: monumental architecture, works of art, minor or popular architecture, military and defensive architecture and witnesses at work, of industrial production, to agricultural culture, to the gastronomic culture.
WHY SHOULD WE PRESERVE CULTURAL HERITAGE?

It is a way of not losing values of cultural identity, which are:
- Cultural
- Artistic
- Historical
- Authenticity
- Antiquity
- Social/functional
- Economic
WHAT SHOULD BE PRESERVED?
- Protection of values
- Physical conservation: matter, construction techniques, shapes, dimensions, colours, materials, textures, character, use, environment and meanings.
- Enhancement
HOW DO WE PRESERVE?
We can preserve by means of :
legislative instruments like
- Protection→ legal actions, administrative rules outside the intervention on the monument itself
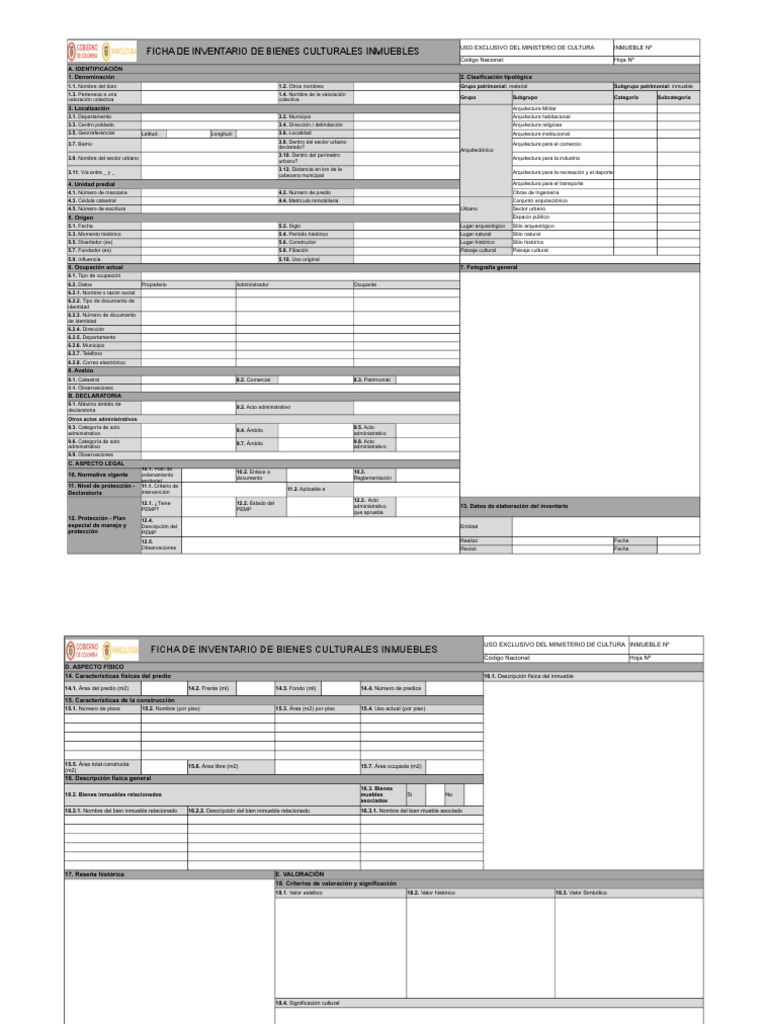
- Inventories → enumeration, location and description of the assets of a specific extent
- Cataloguing→ enumeration, description and location of a property, but also it provides a historical study and economic valuation of a Heritage Resource.
actions of interventions like
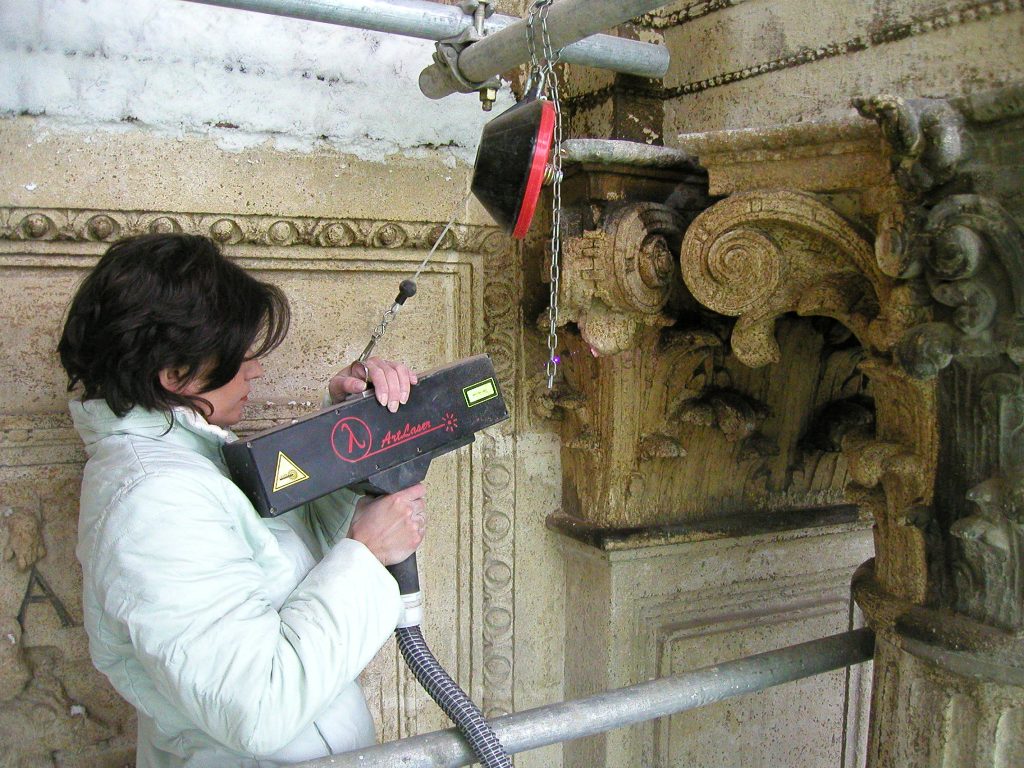
- Preservation of the environment, performing operations to ensure survival against possible damages.
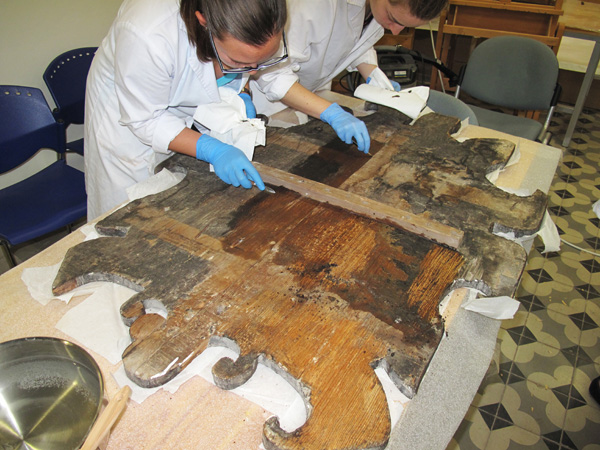
- Maintenance through punctual repairs, in a state of efficiency, in conditions to be used. It is done to maintain it as long as possible the materials that made up the object.
- Repairing the damaged parts of the buildings (roofs, walls, eaves, gutters).
- Consolidation of constructive or material elements by giving them greater solidity.
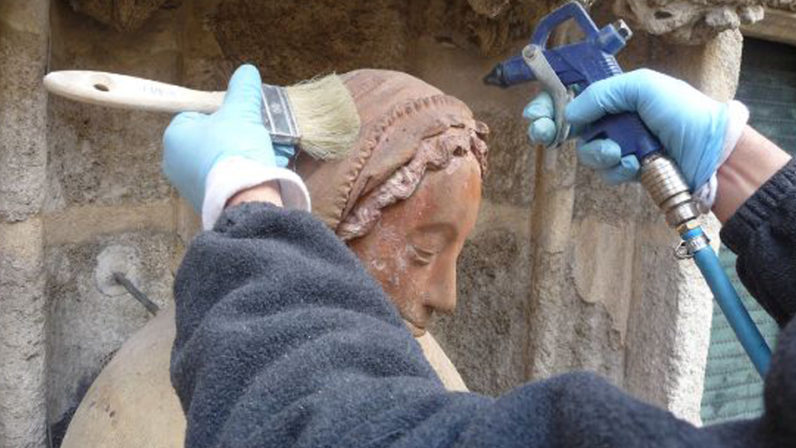
- Renovation in order to improve the aesthetic or legibility lost over time, without any alterations or falsifications of its nature.
- Adaptation to return something to its former state of functionality, adding new ones as well (it is possible).
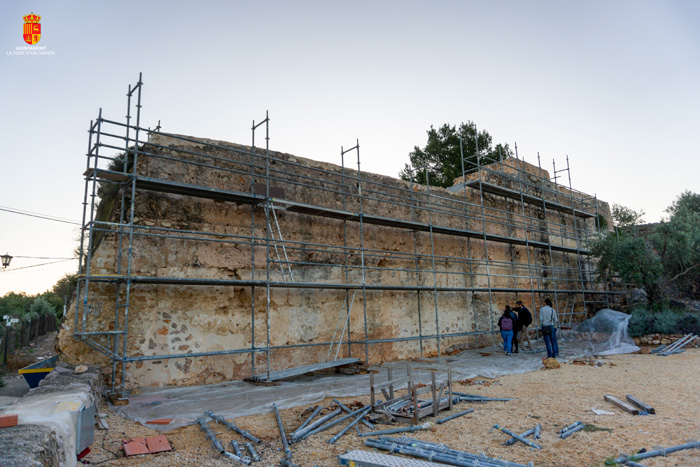
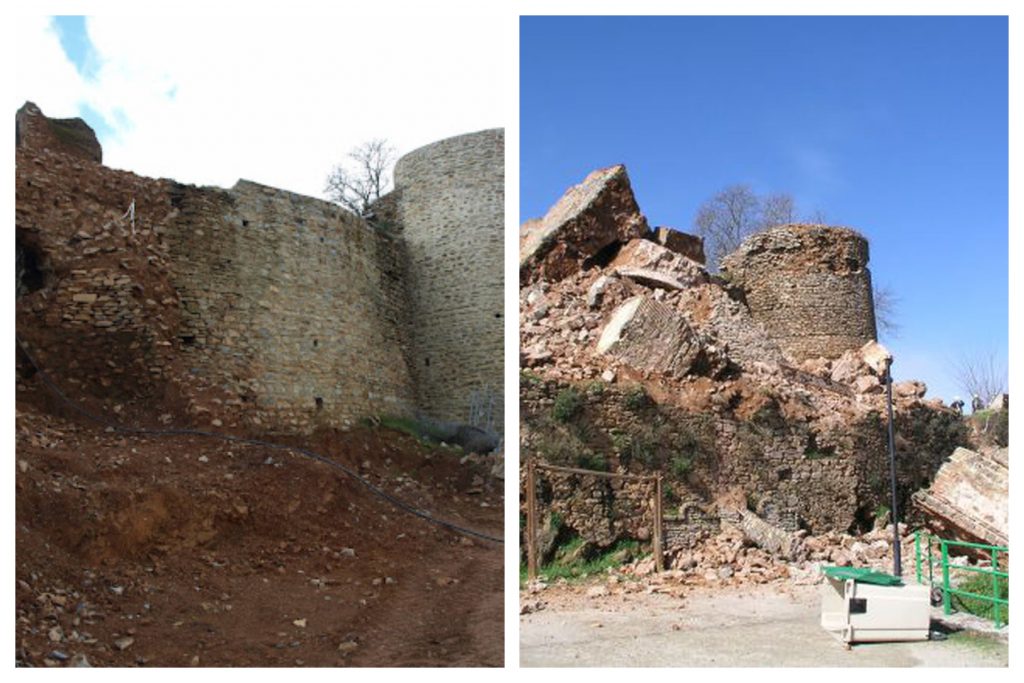
- Reconstruction of a building (partial or integral) due to traumatic events.
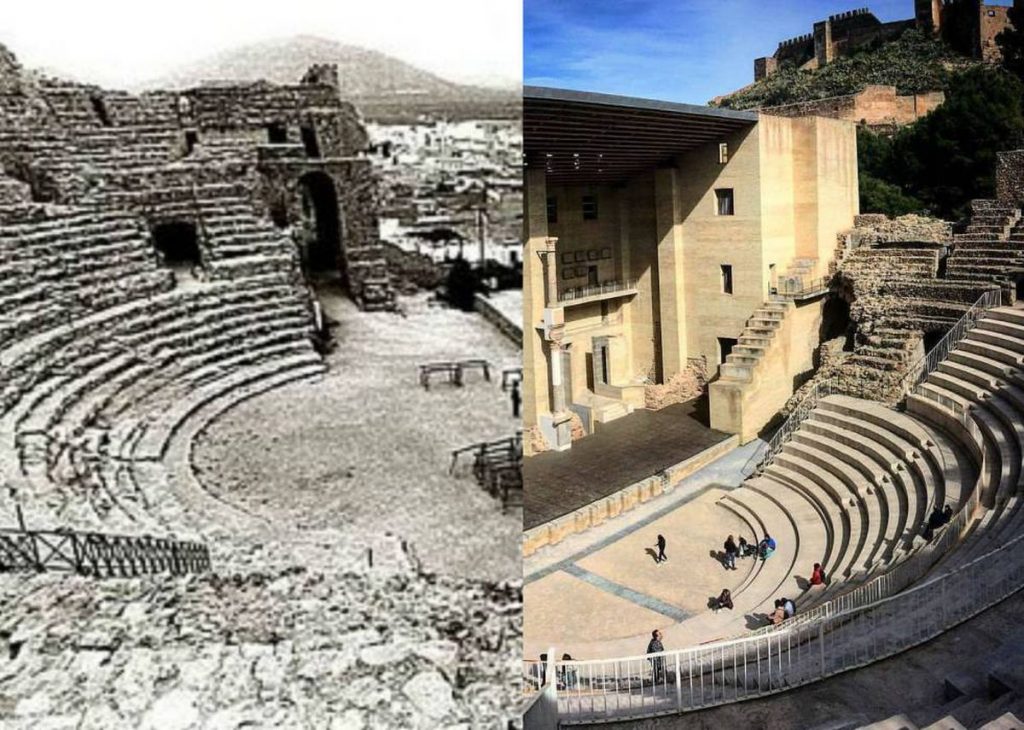
- Anastylosis, which is a technique used in archeology that consists on rebuilding a ruined building or monument.
- Restoration to a former state by eliminating existing elements thet were added later.










Hola, esto es un comentario. Para empezar a moderar, editar y borrar comentarios, por favor, visita la pantalla de comentarios…